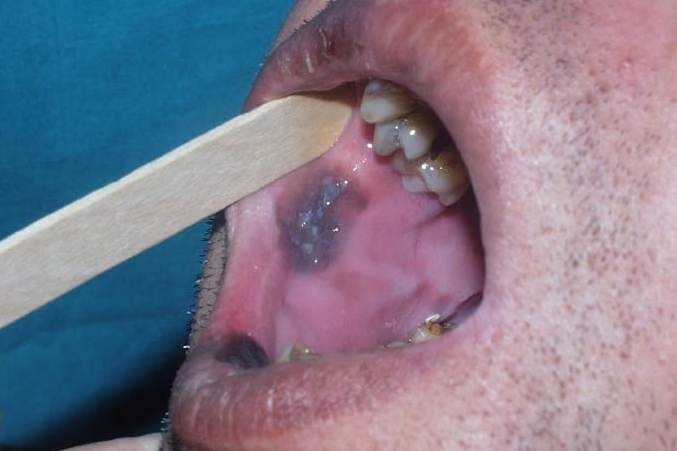
Tongue cancer is a type of oral cancer that can significantly impact daily activities like speaking, eating, and swallowing.
Early detection and treatment are crucial for better outcomes.
Table of content
Toggle🔍 What Is Tongue Cancer?
Tongue cancer occurs when abnormal cells grow uncontrollably on the tongue’s surface. It primarily affects the squamous cells lining the tongue. There are two main types:
- Oral Tongue Cancer: Affects the front two-thirds of the tongue.
- Base of Tongue Cancer: Affects the back one-third of the tongue, part of the oropharynx.
⚠️ Symptoms to Watch For
Early signs of tongue cancer can be subtle. Be alert to:
- A persistent sore or ulcer on the tongue that doesn’t heal.
- A lump or thickening in the tongue.
- Pain or burning sensation on the tongue.
- Red or white patches on the tongue.
- Difficulty swallowing or speaking.
- Numbness in the mouth.
- Unexplained bleeding from the tongue.
If you experience any of these symptoms for more than two weeks, consult a healthcare professional promptly.
🧬 Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing tongue cancer:
- Tobacco Use: Smoking or chewing tobacco significantly raises the risk.
- Alcohol Consumption: Heavy drinking is a known risk factor.
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV): Certain strains are linked to tongue cancer.
- Age and Gender: More common in individuals over 40 and in males.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Neglecting oral health can contribute to risk.
- Diet: A diet low in fruits and vegetables may increase risk.
🧪 Diagnosis
Early diagnosis is vital. Healthcare providers may use:
- Physical Examination: Checking the mouth and throat for abnormalities.
- Biopsy: Removing a tissue sample for laboratory analysis.
- Imaging Tests: CT scans, MRI, or PET scans to determine the extent of cancer.
🩺 Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the cancer’s stage and location:
- Surgery: Removing the tumor and possibly some surrounding tissue.
- Radiation Therapy: Using high-energy rays to kill cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Using drugs to destroy cancer cells, often in combination with radiation.
- Targeted Therapy: Drugs that target specific aspects of cancer cells.
Early-stage cancers may require less aggressive treatment, while advanced stages might need a combination of therapies.
🛡️ Prevention Tips
Reduce your risk by:
- 🚭 Quitting tobacco use.
- 🍷 Limiting alcohol consumption.
- 🥗 Maintaining a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables.
- 🦷 Practicing good oral hygiene.
- 💉 Getting vaccinated against HPV.
- 🦷 Regular dental check-ups for early detection.
📅 When to See a Doctor
If you notice:
- A sore or ulcer on the tongue that doesn’t heal.
- Persistent pain or numbness in the mouth.
- Difficulty swallowing or speaking.
- Unexplained bleeding from the tongue.
Seek medical advice promptly. Early intervention can significantly improve outcomes.
Conclusion
Tongue cancer is a serious but manageable condition when caught early. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options can save lives.
Regular dental visits and a healthy lifestyle are essential for prevention and early detection.
If you notice persistent changes in your tongue or oral health, consult a healthcare professional promptly.
Early action significantly improves outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the early signs of tongue cancer?
Early signs include persistent red or white patches on the tongue, a non-healing sore, or a lump. It may also cause pain when swallowing or speaking.
2. Is tongue cancer curable?
Yes, tongue cancer is often curable, especially when detected early. Treatment success rates are higher for localized cancers that haven’t spread.
3. Can tongue cancer occur without smoking or drinking?
Yes, while tobacco and alcohol use are significant risk factors, tongue cancer can also occur due to genetic predisposition, HPV infection, or unknown causes.
4. Does tongue cancer hurt?
Tongue cancer can cause pain, especially when eating or speaking. Advanced stages may lead to persistent pain even when the tongue is at rest.
5. How does HPV contribute to tongue cancer?
Certain strains of HPV, particularly HPV-16, can cause mutations in cells, leading to cancer. HPV-related tongue cancers often affect the base of the tongue.
6. Can tongue cancer spread to other parts of the body?
Yes, if untreated, tongue cancer can spread to nearby tissues, lymph nodes, and even distant organs like the lungs.
7. What’s the difference between tongue cancer and a tongue ulcer?
Tongue ulcers typically heal within two weeks and are often caused by minor injuries or irritation. Tongue cancer lesions persist and may grow or bleed over time.
8. How can I distinguish tongue cancer symptoms from other oral issues?
Symptoms like persistent sores, unexplained bleeding, and growths on the tongue that don’t heal are more indicative of cancer. Regular dental check-ups can help identify the difference.
9. Are there any visible signs of tongue cancer?
Yes, visible signs include red or white patches, lumps, and sores. In advanced stages, it may cause swelling or deformity of the tongue.
10. How long does it take for tongue cancer to develop?
The development time varies based on individual risk factors. It can take years for pre-cancerous changes to turn into cancer, highlighting the importance of regular check-ups.
11. Can tongue cancer be prevented entirely?
While it cannot be entirely prevented, avoiding known risk factors like smoking, alcohol, and poor oral hygiene can significantly reduce the risk.
12. Should I see a dentist or a doctor if I suspect tongue cancer?
Start with your dentist, as they are trained to spot early signs of oral cancer. They may refer you to a specialist for further diagnosis and treatment.
13. How common is tongue cancer in young adults?
While more common in older adults, tongue cancer can occur in younger individuals, particularly if they have risk factors like HPV infection or a genetic predisposition.
14. Can tongue cancer affect speech?
Yes, depending on the tumor’s size and location, it may impact speech clarity or make speaking difficult.
This information is for educational purposes and should not replace professional medical advice. Consult your healthcare provider for personalized care.
Related Posts
References:
- Sakr, Y., Hamdy, O., Eldeghedi, M., Abdelaziz, R., Alharazin, M., & Awny, S. (2023). Shifting Epidemiology Trends in Tongue Cancer: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Cancers, 15(23), 5680. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15235680
- Papageorge, M. B. (2007). Etiology of Oral Cancer in the Young Patient: Is Tongue Cancer Becoming the Other Cancer in Women? Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Clinics of North America, 19(2), 163-171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coms.2007.01.004
- Kim, G., Choi, S., Youn, S. M., Ko, H., Oh, H. J., Lee, H., Park, Y., & Choi, W. (2022). Treatment outcomes and prognostic factors in oral tongue cancer: A 20-year retrospective study at the National Cancer Center, South Korea. Journal of the Korean Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons, 48(4), 192. https://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2022.48.4.192
- Carolina, A., Da Silva, B. N., Heimlich, F. V., Soares, O. A., Dias, F. L., Henrique, L., De Melo, A. C., Antunes, H. S., Santos Thuler, L. C., & Goldemberg, D. C. (2024). Epidemiological landscape of tongue cancer in younger patients in a National Cancer Center in Brazil. Scientific Reports, 14(1), 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-83470-9